Prvni ulozeni z chegewara githubu
This commit is contained in:
90
libraries/WiFi/examples/FTM/FTM_Initiator/FTM_Initiator.ino
Normal file
90
libraries/WiFi/examples/FTM/FTM_Initiator/FTM_Initiator.ino
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
|
||||
/* Wi-Fi FTM Initiator Arduino Example
|
||||
|
||||
This example code is in the Public Domain (or CC0 licensed, at your option.)
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, this
|
||||
software is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR
|
||||
CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#include "WiFi.h"
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
THIS FEATURE IS SUPPORTED ONLY BY ESP32-S2 AND ESP32-C3
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
// Change the SSID and PASSWORD here if needed
|
||||
const char * WIFI_FTM_SSID = "WiFi_FTM_Responder"; // SSID of AP that has FTM Enabled
|
||||
const char * WIFI_FTM_PASS = "ftm_responder"; // STA Password
|
||||
|
||||
// FTM settings
|
||||
// Number of FTM frames requested in terms of 4 or 8 bursts (allowed values - 0 (No pref), 16, 24, 32, 64)
|
||||
const uint8_t FTM_FRAME_COUNT = 16;
|
||||
// Requested time period between consecutive FTM bursts in 100’s of milliseconds (allowed values - 0 (No pref) or 2-255)
|
||||
const uint16_t FTM_BURST_PERIOD = 2;
|
||||
|
||||
// Semaphore to signal when FTM Report has been received
|
||||
xSemaphoreHandle ftmSemaphore;
|
||||
// Status of the received FTM Report
|
||||
bool ftmSuccess = true;
|
||||
|
||||
// FTM report handler with the calculated data from the round trip
|
||||
void onFtmReport(arduino_event_t *event) {
|
||||
const char * status_str[5] = {"SUCCESS", "UNSUPPORTED", "CONF_REJECTED", "NO_RESPONSE", "FAIL"};
|
||||
wifi_event_ftm_report_t * report = &event->event_info.wifi_ftm_report;
|
||||
// Set the global report status
|
||||
ftmSuccess = report->status == FTM_STATUS_SUCCESS;
|
||||
if (ftmSuccess) {
|
||||
// The estimated distance in meters may vary depending on some factors (see README file)
|
||||
Serial.printf("FTM Estimate: Distance: %.2f m, Return Time: %u ns\n", (float)report->dist_est / 100.0, report->rtt_est);
|
||||
// Pointer to FTM Report with multiple entries, should be freed after use
|
||||
free(report->ftm_report_data);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
Serial.print("FTM Error: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(status_str[report->status]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Signal that report is received
|
||||
xSemaphoreGive(ftmSemaphore);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Initiate FTM Session and wait for FTM Report
|
||||
bool getFtmReport(){
|
||||
if(!WiFi.initiateFTM(FTM_FRAME_COUNT, FTM_BURST_PERIOD)){
|
||||
Serial.println("FTM Error: Initiate Session Failed");
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Wait for signal that report is received and return true if status was success
|
||||
return xSemaphoreTake(ftmSemaphore, portMAX_DELAY) == pdPASS && ftmSuccess;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void setup() {
|
||||
Serial.begin(115200);
|
||||
|
||||
// Create binary semaphore (initialized taken and can be taken/given from any thread/ISR)
|
||||
ftmSemaphore = xSemaphoreCreateBinary();
|
||||
|
||||
// Listen for FTM Report events
|
||||
WiFi.onEvent(onFtmReport, ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_FTM_REPORT);
|
||||
|
||||
// Connect to AP that has FTM Enabled
|
||||
Serial.println("Connecting to FTM Responder");
|
||||
WiFi.begin(WIFI_FTM_SSID, WIFI_FTM_PASS);
|
||||
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
|
||||
delay(500);
|
||||
Serial.print(".");
|
||||
}
|
||||
Serial.println("");
|
||||
Serial.println("WiFi Connected");
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.print("Initiating FTM session with Frame Count ");
|
||||
Serial.print(FTM_FRAME_COUNT);
|
||||
Serial.print(" and Burst Period ");
|
||||
Serial.print(FTM_BURST_PERIOD * 100);
|
||||
Serial.println(" ms");
|
||||
|
||||
// Request FTM reports until one fails
|
||||
while(getFtmReport());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void loop() {
|
||||
delay(1000);
|
||||
}
|
||||
110
libraries/WiFi/examples/FTM/FTM_Initiator/README.md
Normal file
110
libraries/WiFi/examples/FTM/FTM_Initiator/README.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,110 @@
|
||||
# Wi-Fi FTM Initiator Arduino Example
|
||||
|
||||
This example demonstrates how to use the Fine Timing Measurement (FTM) to calculate the distace from the Access Point and the device. This is calculated by the Wi-Fi Round Trip Time (Wi-Fi RTT) introduced on the [IEEE Std 802.11-2016](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_802.11mc) standard.
|
||||
|
||||
This example was based on the [ESP-IDF FTM](https://github.com/espressif/esp-idf/tree/master/examples/wifi/ftm). See the README file for more details about on how to use this feature.
|
||||
|
||||
Some usages for this feature includes:
|
||||
|
||||
* Indoor positioning systems.
|
||||
* Navigation.
|
||||
* Device Location.
|
||||
* Smart Devices.
|
||||
* Alarms.
|
||||
|
||||
# Supported Targets
|
||||
|
||||
Currently, this example supports the following targets:
|
||||
|
||||
| Supported Targets | ESP32-S2 | ESP32-C3 |
|
||||
| ----------------- | -------- | -------- |
|
||||
|
||||
## How to Use Example
|
||||
|
||||
In order to use the FTM, you will need a Responder or Wi-Fi router with FTM capabilities. If you don't own one, you can use a second ESP32-S2 or ESP32-C3 to simulate one.
|
||||
See the **Responder** example to prepare the environment.
|
||||
|
||||
* How to install the Arduino IDE: [Install Arduino IDE](https://github.com/espressif/arduino-esp32/tree/master/docs/arduino-ide).
|
||||
|
||||
### Configure the Project
|
||||
|
||||
To configure this project, you can change the following configuration related to FTM feature:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
// Change the SSID and PASSWORD here if needed
|
||||
const char * WIFI_FTM_SSID = "WiFi_FTM_Responder"; // SSID of AP that has FTM Enabled
|
||||
const char * WIFI_FTM_PASS = "ftm_responder"; // STA Password
|
||||
|
||||
// FTM settings
|
||||
// Number of FTM frames requested in terms of 4 or 8 bursts (allowed values - 0 (No pref), 16, 24, 32, 64)
|
||||
const uint8_t FTM_FRAME_COUNT = 16;
|
||||
// Requested time period between consecutive FTM bursts in 100’s of milliseconds (allowed values - 0 (No pref) or 2-255)
|
||||
const uint16_t FTM_BURST_PERIOD = 2;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* Change the Wi-Fi `SSID` and `PASSWORD` as the same as the Responder/Router.
|
||||
* Change `FTM_FRAME_COUNT` with the number of frames requested to the Responder.
|
||||
* Change `FTM_BURST_PERIOD` with the time between each FTM burst.
|
||||
|
||||
To see more details about FTM, please see the [ESP-IDF docs](https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/latest/esp32s2/api-reference/network/esp_wifi.html).
|
||||
|
||||
#### Using Arduino IDE
|
||||
|
||||
To get more information about the Espressif boards see [Espressif Development Kits](https://www.espressif.com/en/products/devkits).
|
||||
|
||||
* Before Compile/Verify, select the correct board: `Tools -> Board`.
|
||||
* Select the COM port: `Tools -> Port: xxx` where the `xxx` is the detected COM port.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Using Platform IO
|
||||
|
||||
* Select the COM port: `Devices` or setting the `upload_port` option on the `platformio.ini` file.
|
||||
|
||||
## Log Output
|
||||
|
||||
Expected log output:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ESP-ROM:esp32s2-rc4-20191025
|
||||
Build:Oct 25 2019
|
||||
rst:0x1 (POWERON),boot:0x8 (SPI_FAST_FLASH_BOOT)
|
||||
SPIWP:0xee
|
||||
mode:DIO, clock div:1
|
||||
load:0x3ffe6100,len:0x4b0
|
||||
load:0x4004c000,len:0xa6c
|
||||
load:0x40050000,len:0x25c4
|
||||
entry 0x4004c198
|
||||
Connecting to FTM Responder
|
||||
.....
|
||||
WiFi Connected
|
||||
Initiating FTM session with Frame Count 16 and Burst Period 200 ms
|
||||
FTM Estimate: Distance: 0.13 m, Return Time: 0 ns
|
||||
FTM Estimate: Distance: 0.13 m, Return Time: 0 ns
|
||||
FTM Estimate: Distance: 0.13 m, Return Time: 0 ns
|
||||
FTM Estimate: Distance: 0.00 m, Return Time: 0 ns
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Troubleshooting
|
||||
|
||||
***Important: Make sure you are using a good quality USB cable and that you have a reliable power source.***
|
||||
|
||||
* **Programming Fail:** If the programming/flash procedure fails, try reducing the serial connection speed.
|
||||
* **COM port not detected:** Check the USB cable and the USB to Serial driver installation.
|
||||
|
||||
If the error persist, you can ask for help at the official [ESP32 forum](https://esp32.com) or see [Contribute](#contribute).
|
||||
|
||||
## Contribute
|
||||
|
||||
To know how to contribute to this project, see [How to contribute.](https://github.com/espressif/arduino-esp32/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.rst)
|
||||
|
||||
If you have any **feedback** or **issue** to report on this example/library, please open an issue or fix it by creating a new PR. Contributions are more than welcome!
|
||||
|
||||
Before creating a new issue, be sure to try the Troubleshooting and to check if the same issue was already created by someone else.
|
||||
|
||||
## Resources
|
||||
|
||||
* Official ESP32 Forum: [Link](https://esp32.com)
|
||||
* Arduino-ESP32 Official Repository: [espressif/arduino-esp32](https://github.com/espressif/arduino-esp32)
|
||||
* ESP32-S2 Datasheet: [Link to datasheet](https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp32-s2_datasheet_en.pdf)
|
||||
* ESP32-C3 Datasheet: [Link to datasheet](https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp32-c3_datasheet_en.pdf)
|
||||
* Official ESP-IDF documentation: [ESP-IDF](https://idf.espressif.com)
|
||||
23
libraries/WiFi/examples/FTM/FTM_Responder/FTM_Responder.ino
Normal file
23
libraries/WiFi/examples/FTM/FTM_Responder/FTM_Responder.ino
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
/* Wi-Fi FTM Responder Arduino Example
|
||||
|
||||
This example code is in the Public Domain (or CC0 licensed, at your option.)
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, this
|
||||
software is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR
|
||||
CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#include "WiFi.h"
|
||||
// Change the SSID and PASSWORD here if needed
|
||||
const char * WIFI_FTM_SSID = "WiFi_FTM_Responder";
|
||||
const char * WIFI_FTM_PASS = "ftm_responder";
|
||||
|
||||
void setup() {
|
||||
Serial.begin(115200);
|
||||
Serial.println("Starting SoftAP with FTM Responder support");
|
||||
// Enable AP with FTM support (last argument is 'true')
|
||||
WiFi.softAP(WIFI_FTM_SSID, WIFI_FTM_PASS, 1, 0, 4, true);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void loop() {
|
||||
delay(1000);
|
||||
}
|
||||
94
libraries/WiFi/examples/FTM/FTM_Responder/README.md
Normal file
94
libraries/WiFi/examples/FTM/FTM_Responder/README.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,94 @@
|
||||
# Wi-Fi FTM Responder Arduino Example
|
||||
|
||||
This example demonstrates how to use the Fine Timing Measurement (FTM) to calculate the distace from the Access Point and the device. This is calculated by the Wi-Fi Round Trip Time (Wi-Fi RTT) introduced on the [IEEE Std 802.11-2016](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_802.11mc) standard.
|
||||
|
||||
This example will simulate the Router with FTM capability.
|
||||
|
||||
This example was based on the [ESP-IDF FTM](https://github.com/espressif/esp-idf/tree/master/examples/wifi/ftm). See the README file for more details about on how to use this feature.
|
||||
|
||||
Some usages for this feature includes:
|
||||
|
||||
* Indoor positioning systems.
|
||||
* Navigation.
|
||||
* Device Location.
|
||||
* Smart Devices.
|
||||
* Alarms.
|
||||
|
||||
# Supported Targets
|
||||
|
||||
Currently, this example supports the following targets:
|
||||
|
||||
| Supported Targets | ESP32-S2 | ESP32-C3 |
|
||||
| ----------------- | -------- | -------- |
|
||||
|
||||
## How to Use Example
|
||||
|
||||
See the **Initiator** example to prepare the environment.
|
||||
|
||||
* How to install the Arduino IDE: [Install Arduino IDE](https://github.com/espressif/arduino-esp32/tree/master/docs/arduino-ide).
|
||||
|
||||
### Configure the Project
|
||||
|
||||
To configure this project, you can change the following configuration related to STA:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
// Change the SSID and PASSWORD here if needed
|
||||
const char * WIFI_FTM_SSID = "WiFi_FTM_Responder";
|
||||
const char * WIFI_FTM_PASS = "ftm_responder";
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* Change the Wi-Fi `SSID` and `PASSWORD` as the same as the Initiator.
|
||||
|
||||
To see more details about FTM, please see the [ESP-IDF docs](https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/latest/esp32s2/api-reference/network/esp_wifi.html).
|
||||
|
||||
#### Using Arduino IDE
|
||||
|
||||
To get more information about the Espressif boards see [Espressif Development Kits](https://www.espressif.com/en/products/devkits).
|
||||
|
||||
* Before Compile/Verify, select the correct board: `Tools -> Board`.
|
||||
* Select the COM port: `Tools -> Port: xxx` where the `xxx` is the detected COM port.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Using Platform IO
|
||||
|
||||
* Select the COM port: `Devices` or setting the `upload_port` option on the `platformio.ini` file.
|
||||
|
||||
## Log Output
|
||||
|
||||
Expected log output:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Build:Oct 25 2019
|
||||
rst:0x1 (POWERON),boot:0x8 (SPI_FAST_FLASH_BOOT)
|
||||
SPIWP:0xee
|
||||
mode:DIO, clock div:1
|
||||
load:0x3ffe6100,len:0x4b0
|
||||
load:0x4004c000,len:0xa6c
|
||||
load:0x40050000,len:0x25c4
|
||||
entry 0x4004c198
|
||||
Starting SoftAP with FTM Responder support
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Troubleshooting
|
||||
|
||||
***Important: Make sure you are using a good quality USB cable and that you have a reliable power source.***
|
||||
|
||||
* **Programming Fail:** If the programming/flash procedure fails, try reducing the serial connection speed.
|
||||
* **COM port not detected:** Check the USB cable and the USB to Serial driver installation.
|
||||
|
||||
If the error persist, you can ask for help at the official [ESP32 forum](https://esp32.com) or see [Contribute](#contribute).
|
||||
|
||||
## Contribute
|
||||
|
||||
To know how to contribute to this project, see [How to contribute.](https://github.com/espressif/arduino-esp32/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.rst)
|
||||
|
||||
If you have any **feedback** or **issue** to report on this example/library, please open an issue or fix it by creating a new PR. Contributions are more than welcome!
|
||||
|
||||
Before creating a new issue, be sure to try the Troubleshooting and to check if the same issue was already created by someone else.
|
||||
|
||||
## Resources
|
||||
|
||||
* Official ESP32 Forum: [Link](https://esp32.com)
|
||||
* Arduino-ESP32 Official Repository: [espressif/arduino-esp32](https://github.com/espressif/arduino-esp32)
|
||||
* ESP32-S2 Datasheet: [Link to datasheet](https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp32-s2_datasheet_en.pdf)
|
||||
* ESP32-C3 Datasheet: [Link to datasheet](https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp32-c3_datasheet_en.pdf)
|
||||
* Official ESP-IDF documentation: [ESP-IDF](https://idf.espressif.com)
|
||||
116
libraries/WiFi/examples/SimpleWiFiServer/SimpleWiFiServer.ino
Normal file
116
libraries/WiFi/examples/SimpleWiFiServer/SimpleWiFiServer.ino
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,116 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
WiFi Web Server LED Blink
|
||||
|
||||
A simple web server that lets you blink an LED via the web.
|
||||
This sketch will print the IP address of your WiFi Shield (once connected)
|
||||
to the Serial monitor. From there, you can open that address in a web browser
|
||||
to turn on and off the LED on pin 5.
|
||||
|
||||
If the IP address of your shield is yourAddress:
|
||||
http://yourAddress/H turns the LED on
|
||||
http://yourAddress/L turns it off
|
||||
|
||||
This example is written for a network using WPA2 encryption. For insecure
|
||||
WEP or WPA, change the Wifi.begin() call and use Wifi.setMinSecurity() accordingly.
|
||||
|
||||
Circuit:
|
||||
* WiFi shield attached
|
||||
* LED attached to pin 5
|
||||
|
||||
created for arduino 25 Nov 2012
|
||||
by Tom Igoe
|
||||
|
||||
ported for sparkfun esp32
|
||||
31.01.2017 by Jan Hendrik Berlin
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <WiFi.h>
|
||||
|
||||
const char* ssid = "yourssid";
|
||||
const char* password = "yourpasswd";
|
||||
|
||||
WiFiServer server(80);
|
||||
|
||||
void setup()
|
||||
{
|
||||
Serial.begin(115200);
|
||||
pinMode(5, OUTPUT); // set the LED pin mode
|
||||
|
||||
delay(10);
|
||||
|
||||
// We start by connecting to a WiFi network
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.println();
|
||||
Serial.println();
|
||||
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
|
||||
Serial.println(ssid);
|
||||
|
||||
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
|
||||
|
||||
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
|
||||
delay(500);
|
||||
Serial.print(".");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.println("");
|
||||
Serial.println("WiFi connected.");
|
||||
Serial.println("IP address: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
|
||||
|
||||
server.begin();
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int value = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
void loop(){
|
||||
WiFiClient client = server.available(); // listen for incoming clients
|
||||
|
||||
if (client) { // if you get a client,
|
||||
Serial.println("New Client."); // print a message out the serial port
|
||||
String currentLine = ""; // make a String to hold incoming data from the client
|
||||
while (client.connected()) { // loop while the client's connected
|
||||
if (client.available()) { // if there's bytes to read from the client,
|
||||
char c = client.read(); // read a byte, then
|
||||
Serial.write(c); // print it out the serial monitor
|
||||
if (c == '\n') { // if the byte is a newline character
|
||||
|
||||
// if the current line is blank, you got two newline characters in a row.
|
||||
// that's the end of the client HTTP request, so send a response:
|
||||
if (currentLine.length() == 0) {
|
||||
// HTTP headers always start with a response code (e.g. HTTP/1.1 200 OK)
|
||||
// and a content-type so the client knows what's coming, then a blank line:
|
||||
client.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");
|
||||
client.println("Content-type:text/html");
|
||||
client.println();
|
||||
|
||||
// the content of the HTTP response follows the header:
|
||||
client.print("Click <a href=\"/H\">here</a> to turn the LED on pin 5 on.<br>");
|
||||
client.print("Click <a href=\"/L\">here</a> to turn the LED on pin 5 off.<br>");
|
||||
|
||||
// The HTTP response ends with another blank line:
|
||||
client.println();
|
||||
// break out of the while loop:
|
||||
break;
|
||||
} else { // if you got a newline, then clear currentLine:
|
||||
currentLine = "";
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if (c != '\r') { // if you got anything else but a carriage return character,
|
||||
currentLine += c; // add it to the end of the currentLine
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Check to see if the client request was "GET /H" or "GET /L":
|
||||
if (currentLine.endsWith("GET /H")) {
|
||||
digitalWrite(5, HIGH); // GET /H turns the LED on
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (currentLine.endsWith("GET /L")) {
|
||||
digitalWrite(5, LOW); // GET /L turns the LED off
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// close the connection:
|
||||
client.stop();
|
||||
Serial.println("Client Disconnected.");
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
104
libraries/WiFi/examples/WPS/README.md
Normal file
104
libraries/WiFi/examples/WPS/README.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,104 @@
|
||||
Example Serial Logs For Various Cases
|
||||
======================================
|
||||
|
||||
For WPS Push Button method,after the ESP32 boots up and prints that WPS has started, press the button that looks something like [this](https://www.verizon.com/supportresources/images/fqgrouter-frontview-wps-button.png) on your router. In case you dont find anything similar, check your router specs if it does really support WPS Push functionality.
|
||||
|
||||
As for WPS Pin Mode, it will output a 8 digit Pin on the Serial Monitor that will change every 2 minutes if it hasn't connected. You need to log in to your router (generally reaching 192.168.0.1) and enter the pin shown in Serial Monitor in the WPS Settings of your router.
|
||||
|
||||
#### WPS Push Button Failure
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ets Jun 8 2016 00:22:57
|
||||
|
||||
rst:0x10 (RTCWDT_RTC_RESET),boot:0x13 (SPI_FAST_FLASH_BOOT)
|
||||
configsip: 0, SPIWP:0xee
|
||||
clk_drv:0x00,q_drv:0x00,d_drv:0x00,cs0_drv:0x00,hd_drv:0x00,wp_drv:0x00
|
||||
mode:DIO, clock div:1
|
||||
load:0x3fff0010,len:4
|
||||
load:0x3fff0014,len:732
|
||||
load:0x40078000,len:0
|
||||
load:0x40078000,len:11572
|
||||
entry 0x40078a14
|
||||
|
||||
Starting WPS
|
||||
Station Mode Started
|
||||
WPS Timedout, retrying
|
||||
WPS Timedout, retrying
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### WPS Push Button Successfull
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ets Jun 8 2016 00:22:57
|
||||
|
||||
rst:0x1 (POWERON_RESET),boot:0x13 (SPI_FAST_FLASH_BOOT)
|
||||
ets Jun 8 2016 00:22:57
|
||||
|
||||
rst:0x10 (RTCWDT_RTC_RESET),boot:0x13 (SPI_FAST_FLASH_BOOT)
|
||||
configsip: 0, SPIWP:0xee
|
||||
clk_drv:0x00,q_drv:0x00,d_drv:0x00,cs0_drv:0x00,hd_drv:0x00,wp_drv:0x00
|
||||
mode:DIO, clock div:1
|
||||
load:0x3fff0010,len:4
|
||||
load:0x3fff0014,len:732
|
||||
load:0x40078000,len:0
|
||||
load:0x40078000,len:11572
|
||||
entry 0x40078a14
|
||||
|
||||
Starting WPS
|
||||
Station Mode Started
|
||||
WPS Successfull, stopping WPS and connecting to: < Your Router SSID >
|
||||
Disconnected from station, attempting reconnection
|
||||
Connected to : < Your Router SSID >
|
||||
Got IP: 192.168.1.100
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### WPS PIN Failure
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ets Jun 8 2016 00:22:57
|
||||
|
||||
rst:0x1 (POWERON_RESET),boot:0x13 (SPI_FAST_FLASH_BOOT)
|
||||
ets Jun 8 2016 00:22:57
|
||||
|
||||
rst:0x10 (RTCWDT_RTC_RESET),boot:0x13 (SPI_FAST_FLASH_BOOT)
|
||||
configsip: 0, SPIWP:0xee
|
||||
clk_drv:0x00,q_drv:0x00,d_drv:0x00,cs0_drv:0x00,hd_drv:0x00,wp_drv:0x00
|
||||
mode:DIO, clock div:1
|
||||
load:0x3fff0010,len:4
|
||||
load:0x3fff0014,len:732
|
||||
load:0x40078000,len:0
|
||||
load:0x40078000,len:11572
|
||||
entry 0x40078a14
|
||||
|
||||
Starting WPS
|
||||
Station Mode Started
|
||||
WPS_PIN = 94842104
|
||||
WPS Timedout, retrying
|
||||
WPS_PIN = 55814171
|
||||
WPS Timedout, retrying
|
||||
WPS_PIN = 71321622
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### WPS PIN Successfull
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ets Jun 8 2016 00:22:57
|
||||
|
||||
rst:0x10 (RTCWDT_RTC_RESET),boot:0x13 (SPI_FAST_FLASH_BOOT)
|
||||
configsip: 0, SPIWP:0xee
|
||||
clk_drv:0x00,q_drv:0x00,d_drv:0x00,cs0_drv:0x00,hd_drv:0x00,wp_drv:0x00
|
||||
mode:DIO, clock div:1
|
||||
load:0x3fff0010,len:4
|
||||
load:0x3fff0014,len:732
|
||||
load:0x40078000,len:0
|
||||
load:0x40078000,len:11572
|
||||
entry 0x40078a14
|
||||
|
||||
Starting WPS
|
||||
Station Mode Started
|
||||
WPS_PIN = 36807581
|
||||
WPS Successfull, stopping WPS and connecting to: <Your Router SSID>
|
||||
Disconnected from station, attempting reconnection
|
||||
Connected to :<Your Router SSID>
|
||||
Got IP: 192.168.1.100
|
||||
```
|
||||
115
libraries/WiFi/examples/WPS/WPS.ino
Normal file
115
libraries/WiFi/examples/WPS/WPS.ino
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Example Code To Get ESP32 To Connect To A Router Using WPS
|
||||
===========================================================
|
||||
This example code provides both Push Button method and Pin
|
||||
based WPS entry to get your ESP connected to your WiFi router.
|
||||
|
||||
Hardware Requirements
|
||||
========================
|
||||
ESP32 and a Router having WPS functionality
|
||||
|
||||
This code is under Public Domain License.
|
||||
|
||||
Author:
|
||||
Pranav Cherukupalli <cherukupallip@gmail.com>
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include "WiFi.h"
|
||||
#include "esp_wps.h"
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Change the definition of the WPS mode
|
||||
from WPS_TYPE_PBC to WPS_TYPE_PIN in
|
||||
the case that you are using pin type
|
||||
WPS
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#define ESP_WPS_MODE WPS_TYPE_PBC
|
||||
#define ESP_MANUFACTURER "ESPRESSIF"
|
||||
#define ESP_MODEL_NUMBER "ESP32"
|
||||
#define ESP_MODEL_NAME "ESPRESSIF IOT"
|
||||
#define ESP_DEVICE_NAME "ESP STATION"
|
||||
|
||||
static esp_wps_config_t config;
|
||||
|
||||
void wpsInitConfig(){
|
||||
config.wps_type = ESP_WPS_MODE;
|
||||
strcpy(config.factory_info.manufacturer, ESP_MANUFACTURER);
|
||||
strcpy(config.factory_info.model_number, ESP_MODEL_NUMBER);
|
||||
strcpy(config.factory_info.model_name, ESP_MODEL_NAME);
|
||||
strcpy(config.factory_info.device_name, ESP_DEVICE_NAME);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void wpsStart(){
|
||||
if(esp_wifi_wps_enable(&config)){
|
||||
Serial.println("WPS Enable Failed");
|
||||
} else if(esp_wifi_wps_start(0)){
|
||||
Serial.println("WPS Start Failed");
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void wpsStop(){
|
||||
if(esp_wifi_wps_disable()){
|
||||
Serial.println("WPS Disable Failed");
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
String wpspin2string(uint8_t a[]){
|
||||
char wps_pin[9];
|
||||
for(int i=0;i<8;i++){
|
||||
wps_pin[i] = a[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
wps_pin[8] = '\0';
|
||||
return (String)wps_pin;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void WiFiEvent(WiFiEvent_t event, arduino_event_info_t info){
|
||||
switch(event){
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_START:
|
||||
Serial.println("Station Mode Started");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_GOT_IP:
|
||||
Serial.println("Connected to :" + String(WiFi.SSID()));
|
||||
Serial.print("Got IP: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_DISCONNECTED:
|
||||
Serial.println("Disconnected from station, attempting reconnection");
|
||||
WiFi.reconnect();
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WPS_ER_SUCCESS:
|
||||
Serial.println("WPS Successfull, stopping WPS and connecting to: " + String(WiFi.SSID()));
|
||||
wpsStop();
|
||||
delay(10);
|
||||
WiFi.begin();
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WPS_ER_FAILED:
|
||||
Serial.println("WPS Failed, retrying");
|
||||
wpsStop();
|
||||
wpsStart();
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WPS_ER_TIMEOUT:
|
||||
Serial.println("WPS Timedout, retrying");
|
||||
wpsStop();
|
||||
wpsStart();
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WPS_ER_PIN:
|
||||
Serial.println("WPS_PIN = " + wpspin2string(info.wps_er_pin.pin_code));
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void setup(){
|
||||
Serial.begin(115200);
|
||||
delay(10);
|
||||
Serial.println();
|
||||
WiFi.onEvent(WiFiEvent);
|
||||
WiFi.mode(WIFI_MODE_STA);
|
||||
Serial.println("Starting WPS");
|
||||
wpsInitConfig();
|
||||
wpsStart();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void loop(){
|
||||
//nothing to do here
|
||||
}
|
||||
93
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiAccessPoint/WiFiAccessPoint.ino
Normal file
93
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiAccessPoint/WiFiAccessPoint.ino
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
WiFiAccessPoint.ino creates a WiFi access point and provides a web server on it.
|
||||
|
||||
Steps:
|
||||
1. Connect to the access point "yourAp"
|
||||
2. Point your web browser to http://192.168.4.1/H to turn the LED on or http://192.168.4.1/L to turn it off
|
||||
OR
|
||||
Run raw TCP "GET /H" and "GET /L" on PuTTY terminal with 192.168.4.1 as IP address and 80 as port
|
||||
|
||||
Created for arduino-esp32 on 04 July, 2018
|
||||
by Elochukwu Ifediora (fedy0)
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <WiFi.h>
|
||||
#include <WiFiClient.h>
|
||||
#include <WiFiAP.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#define LED_BUILTIN 2 // Set the GPIO pin where you connected your test LED or comment this line out if your dev board has a built-in LED
|
||||
|
||||
// Set these to your desired credentials.
|
||||
const char *ssid = "yourAP";
|
||||
const char *password = "yourPassword";
|
||||
|
||||
WiFiServer server(80);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
void setup() {
|
||||
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT);
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.begin(115200);
|
||||
Serial.println();
|
||||
Serial.println("Configuring access point...");
|
||||
|
||||
// You can remove the password parameter if you want the AP to be open.
|
||||
WiFi.softAP(ssid, password);
|
||||
IPAddress myIP = WiFi.softAPIP();
|
||||
Serial.print("AP IP address: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(myIP);
|
||||
server.begin();
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.println("Server started");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void loop() {
|
||||
WiFiClient client = server.available(); // listen for incoming clients
|
||||
|
||||
if (client) { // if you get a client,
|
||||
Serial.println("New Client."); // print a message out the serial port
|
||||
String currentLine = ""; // make a String to hold incoming data from the client
|
||||
while (client.connected()) { // loop while the client's connected
|
||||
if (client.available()) { // if there's bytes to read from the client,
|
||||
char c = client.read(); // read a byte, then
|
||||
Serial.write(c); // print it out the serial monitor
|
||||
if (c == '\n') { // if the byte is a newline character
|
||||
|
||||
// if the current line is blank, you got two newline characters in a row.
|
||||
// that's the end of the client HTTP request, so send a response:
|
||||
if (currentLine.length() == 0) {
|
||||
// HTTP headers always start with a response code (e.g. HTTP/1.1 200 OK)
|
||||
// and a content-type so the client knows what's coming, then a blank line:
|
||||
client.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");
|
||||
client.println("Content-type:text/html");
|
||||
client.println();
|
||||
|
||||
// the content of the HTTP response follows the header:
|
||||
client.print("Click <a href=\"/H\">here</a> to turn ON the LED.<br>");
|
||||
client.print("Click <a href=\"/L\">here</a> to turn OFF the LED.<br>");
|
||||
|
||||
// The HTTP response ends with another blank line:
|
||||
client.println();
|
||||
// break out of the while loop:
|
||||
break;
|
||||
} else { // if you got a newline, then clear currentLine:
|
||||
currentLine = "";
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if (c != '\r') { // if you got anything else but a carriage return character,
|
||||
currentLine += c; // add it to the end of the currentLine
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Check to see if the client request was "GET /H" or "GET /L":
|
||||
if (currentLine.endsWith("GET /H")) {
|
||||
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH); // GET /H turns the LED on
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (currentLine.endsWith("GET /L")) {
|
||||
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW); // GET /L turns the LED off
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// close the connection:
|
||||
client.stop();
|
||||
Serial.println("Client Disconnected.");
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,128 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015-2016 Espressif Systems (Shanghai) PTE LTD
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
// Sketch shows how to switch between WiFi and BlueTooth or use both
|
||||
// Button is attached between GPIO 0 and GND and modes are switched with each press
|
||||
|
||||
#include "WiFi.h"
|
||||
#define STA_SSID "your-ssid"
|
||||
#define STA_PASS "your-pass"
|
||||
#define AP_SSID "esp32"
|
||||
|
||||
enum { STEP_BTON, STEP_BTOFF, STEP_STA, STEP_AP, STEP_AP_STA, STEP_OFF, STEP_BT_STA, STEP_END };
|
||||
|
||||
void onButton(){
|
||||
static uint32_t step = STEP_BTON;
|
||||
switch(step){
|
||||
case STEP_BTON://BT Only
|
||||
Serial.println("** Starting BT");
|
||||
btStart();
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case STEP_BTOFF://All Off
|
||||
Serial.println("** Stopping BT");
|
||||
btStop();
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case STEP_STA://STA Only
|
||||
Serial.println("** Starting STA");
|
||||
WiFi.begin(STA_SSID, STA_PASS);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case STEP_AP://AP Only
|
||||
Serial.println("** Stopping STA");
|
||||
WiFi.mode(WIFI_AP);
|
||||
Serial.println("** Starting AP");
|
||||
WiFi.softAP(AP_SSID);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case STEP_AP_STA://AP+STA
|
||||
Serial.println("** Starting STA");
|
||||
WiFi.begin(STA_SSID, STA_PASS);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case STEP_OFF://All Off
|
||||
Serial.println("** Stopping WiFi");
|
||||
WiFi.mode(WIFI_OFF);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case STEP_BT_STA://BT+STA
|
||||
Serial.println("** Starting STA+BT");
|
||||
WiFi.begin(STA_SSID, STA_PASS);
|
||||
btStart();
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case STEP_END://All Off
|
||||
Serial.println("** Stopping WiFi+BT");
|
||||
WiFi.mode(WIFI_OFF);
|
||||
btStop();
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(step == STEP_END){
|
||||
step = STEP_BTON;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
step++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
//little debounce
|
||||
delay(100);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void WiFiEvent(WiFiEvent_t event){
|
||||
switch(event) {
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_AP_START:
|
||||
Serial.println("AP Started");
|
||||
WiFi.softAPsetHostname(AP_SSID);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_AP_STOP:
|
||||
Serial.println("AP Stopped");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_START:
|
||||
Serial.println("STA Started");
|
||||
WiFi.setHostname(AP_SSID);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_CONNECTED:
|
||||
Serial.println("STA Connected");
|
||||
WiFi.enableIpV6();
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_GOT_IP6:
|
||||
Serial.print("STA IPv6: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(WiFi.localIPv6());
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_GOT_IP:
|
||||
Serial.print("STA IPv4: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_DISCONNECTED:
|
||||
Serial.println("STA Disconnected");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_STOP:
|
||||
Serial.println("STA Stopped");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void setup() {
|
||||
Serial.begin(115200);
|
||||
pinMode(0, INPUT_PULLUP);
|
||||
WiFi.onEvent(WiFiEvent);
|
||||
Serial.print("ESP32 SDK: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(ESP.getSdkVersion());
|
||||
Serial.println("Press the button to select the next mode");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void loop() {
|
||||
static uint8_t lastPinState = 1;
|
||||
uint8_t pinState = digitalRead(0);
|
||||
if(!pinState && lastPinState){
|
||||
onButton();
|
||||
}
|
||||
lastPinState = pinState;
|
||||
}
|
||||
94
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiClient/WiFiClient.ino
Normal file
94
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiClient/WiFiClient.ino
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,94 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* This sketch sends data via HTTP GET requests to data.sparkfun.com service.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* You need to get streamId and privateKey at data.sparkfun.com and paste them
|
||||
* below. Or just customize this script to talk to other HTTP servers.
|
||||
*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <WiFi.h>
|
||||
|
||||
const char* ssid = "your-ssid";
|
||||
const char* password = "your-password";
|
||||
|
||||
const char* host = "data.sparkfun.com";
|
||||
const char* streamId = "....................";
|
||||
const char* privateKey = "....................";
|
||||
|
||||
void setup()
|
||||
{
|
||||
Serial.begin(115200);
|
||||
delay(10);
|
||||
|
||||
// We start by connecting to a WiFi network
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.println();
|
||||
Serial.println();
|
||||
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
|
||||
Serial.println(ssid);
|
||||
|
||||
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
|
||||
|
||||
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
|
||||
delay(500);
|
||||
Serial.print(".");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.println("");
|
||||
Serial.println("WiFi connected");
|
||||
Serial.println("IP address: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int value = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
void loop()
|
||||
{
|
||||
delay(5000);
|
||||
++value;
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.print("connecting to ");
|
||||
Serial.println(host);
|
||||
|
||||
// Use WiFiClient class to create TCP connections
|
||||
WiFiClient client;
|
||||
const int httpPort = 80;
|
||||
if (!client.connect(host, httpPort)) {
|
||||
Serial.println("connection failed");
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// We now create a URI for the request
|
||||
String url = "/input/";
|
||||
url += streamId;
|
||||
url += "?private_key=";
|
||||
url += privateKey;
|
||||
url += "&value=";
|
||||
url += value;
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.print("Requesting URL: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(url);
|
||||
|
||||
// This will send the request to the server
|
||||
client.print(String("GET ") + url + " HTTP/1.1\r\n" +
|
||||
"Host: " + host + "\r\n" +
|
||||
"Connection: close\r\n\r\n");
|
||||
unsigned long timeout = millis();
|
||||
while (client.available() == 0) {
|
||||
if (millis() - timeout > 5000) {
|
||||
Serial.println(">>> Client Timeout !");
|
||||
client.stop();
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Read all the lines of the reply from server and print them to Serial
|
||||
while(client.available()) {
|
||||
String line = client.readStringUntil('\r');
|
||||
Serial.print(line);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.println();
|
||||
Serial.println("closing connection");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
87
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiClientBasic/WiFiClientBasic.ino
Normal file
87
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiClientBasic/WiFiClientBasic.ino
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* This sketch sends a message to a TCP server
|
||||
*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <WiFi.h>
|
||||
#include <WiFiMulti.h>
|
||||
|
||||
WiFiMulti WiFiMulti;
|
||||
|
||||
void setup()
|
||||
{
|
||||
Serial.begin(115200);
|
||||
delay(10);
|
||||
|
||||
// We start by connecting to a WiFi network
|
||||
WiFiMulti.addAP("SSID", "passpasspass");
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.println();
|
||||
Serial.println();
|
||||
Serial.print("Waiting for WiFi... ");
|
||||
|
||||
while(WiFiMulti.run() != WL_CONNECTED) {
|
||||
Serial.print(".");
|
||||
delay(500);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.println("");
|
||||
Serial.println("WiFi connected");
|
||||
Serial.println("IP address: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
|
||||
|
||||
delay(500);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
void loop()
|
||||
{
|
||||
// const uint16_t port = 80;
|
||||
// const char * host = "192.168.1.1"; // ip or dns
|
||||
const uint16_t port = 1337;
|
||||
const char * host = "192.168.1.10"; // ip or dns
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
|
||||
Serial.println(host);
|
||||
|
||||
// Use WiFiClient class to create TCP connections
|
||||
WiFiClient client;
|
||||
|
||||
if (!client.connect(host, port)) {
|
||||
Serial.println("Connection failed.");
|
||||
Serial.println("Waiting 5 seconds before retrying...");
|
||||
delay(5000);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// This will send a request to the server
|
||||
//uncomment this line to send an arbitrary string to the server
|
||||
//client.print("Send this data to the server");
|
||||
//uncomment this line to send a basic document request to the server
|
||||
client.print("GET /index.html HTTP/1.1\n\n");
|
||||
|
||||
int maxloops = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
//wait for the server's reply to become available
|
||||
while (!client.available() && maxloops < 1000)
|
||||
{
|
||||
maxloops++;
|
||||
delay(1); //delay 1 msec
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (client.available() > 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
//read back one line from the server
|
||||
String line = client.readStringUntil('\r');
|
||||
Serial.println(line);
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
Serial.println("client.available() timed out ");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.println("Closing connection.");
|
||||
client.stop();
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.println("Waiting 5 seconds before restarting...");
|
||||
delay(5000);
|
||||
}
|
||||
43
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiClientEnterprise/README.md
Normal file
43
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiClientEnterprise/README.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
# ESP32-Eduroam
|
||||
* Eduroam wifi connection with university login identity
|
||||
* Working under Eduroam networks worldwide
|
||||
* Methods: PEAP + MsCHAPv2
|
||||
|
||||
# Format
|
||||
* IDENTITY = youridentity --> if connecting from different university, use youridentity@youruniversity.domain format
|
||||
* PASSWORD = yourpassword
|
||||
|
||||
# Usage
|
||||
* Change IDENTITY
|
||||
* Change password
|
||||
* Upload sketch and enjoy!
|
||||
* After sucessful assign of IP address, board will connect to HTTP page on internet to verify your authentification
|
||||
* Board will auto reconnect to Eduroam if it lost connection
|
||||
|
||||
# Tested locations
|
||||
|University|Board|Method|Result|
|
||||
|-------------|-------------| -----|------|
|
||||
|Technical University in Košice (Slovakia)|ESP32 Devkit v1|PEAP + MsCHAPv2|Working|
|
||||
|Technical University in Košice (Slovakia)|ESP32 Devmodule v4|PEAP + MsCHAPv2|Working on 6th attempt in loop|
|
||||
|Slovak Technical University in Bratislava (Slovakia)|ESP32 Devkit v1|PEAP + MsCHAPv2|Working|
|
||||
|University of Antwerp (Belgium)|Lolin32|PEAP + MsCHAPv2|Working|
|
||||
|UPV Universitat Politècnica de València (Spain)|ESP32 Devmodule v4|PEAP + MsCHAPv2|Working|
|
||||
|Local Zeroshell powered network|ESP32 Devkit v1|PEAP + MsCHAPv2|*Not working*|
|
||||
|Hasselt University (Belgium)|xxx|PEAP + MsCHAPv2|Working with fix sketch|
|
||||
|Universidad de Granada (Spain)|Lolin D32 Pro|PEAP + MsCHAPv2|Working|
|
||||
|Universidad de Granada (Spain)|Lolin D32|PEAP + MsCHAPv2|Working|
|
||||
|Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina (Brazil)|xxx|EAP-TTLS + MsCHAPv2|Working|
|
||||
|University of Central Florida (Orlando, Florida)|ESP32 Built-in OLED – Heltec WiFi Kit 32|PEAP + MsCHAPv2|Working|
|
||||
|Université de Montpellier (France)|NodeMCU-32S|PEAP + MsCHAPv2|Working|
|
||||
|
||||
# Common errors - Switch to Debug mode for Serial monitor prints
|
||||
|Error|Appearance|Solution|
|
||||
|-------------|-------------|-------------|
|
||||
|wifi: Set status to INIT|Frequent|Hold EN button for few seconds|
|
||||
|HANDSHAKE_TIMEOUT|Rare|Bug was found under Zeroshell RADIUS authentization - Unsucessful connection|
|
||||
|AUTH_EXPIRE|Common|In the case of weak wifi network signal, this error is quite common, bring your device closer to AP|
|
||||
|ASSOC_EXPIRE|Rare|-|
|
||||
# Sucessful connection example
|
||||
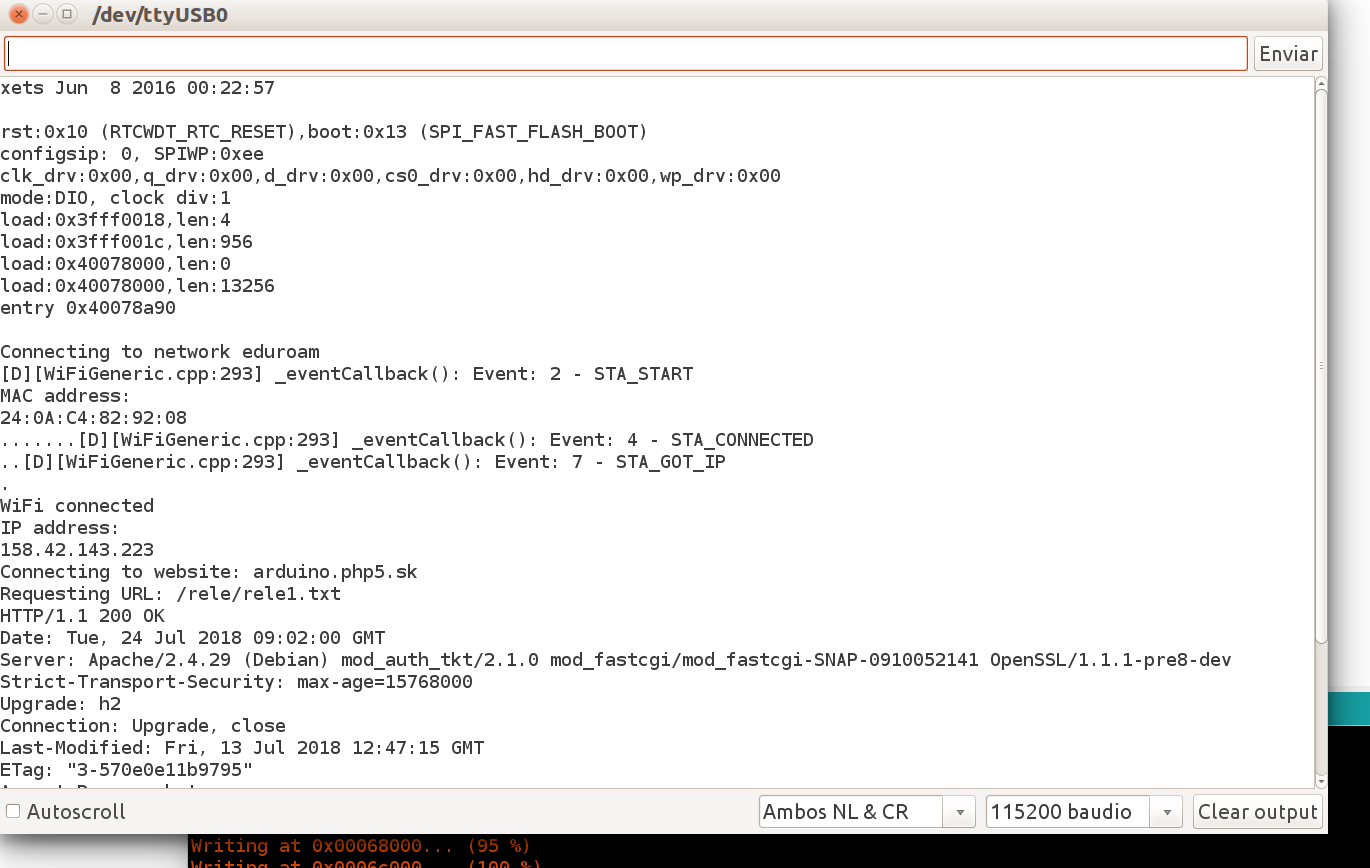
|
||||
# Unsucessful connection example
|
||||

|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
|
||||
#include <WiFi.h> //Wifi library
|
||||
#include "esp_wpa2.h" //wpa2 library for connections to Enterprise networks
|
||||
#define EAP_IDENTITY "login" //if connecting from another corporation, use identity@organisation.domain in Eduroam
|
||||
#define EAP_USERNAME "login" //oftentimes just a repeat of the identity
|
||||
#define EAP_PASSWORD "password" //your Eduroam password
|
||||
const char* ssid = "eduroam"; // Eduroam SSID
|
||||
const char* host = "arduino.php5.sk"; //external server domain for HTTP connection after authentification
|
||||
int counter = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
// NOTE: For some systems, various certification keys are required to connect to the wifi system.
|
||||
// Usually you are provided these by the IT department of your organization when certs are required
|
||||
// and you can't connect with just an identity and password.
|
||||
// Most eduroam setups we have seen do not require this level of authentication, but you should contact
|
||||
// your IT department to verify.
|
||||
// You should uncomment these and populate with the contents of the files if this is required for your scenario (See Example 2 and Example 3 below).
|
||||
//const char *ca_pem = "insert your CA cert from your .pem file here";
|
||||
//const char *client_cert = "insert your client cert from your .crt file here";
|
||||
//const char *client_key = "insert your client key from your .key file here";
|
||||
|
||||
void setup() {
|
||||
Serial.begin(115200);
|
||||
delay(10);
|
||||
Serial.println();
|
||||
Serial.print("Connecting to network: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(ssid);
|
||||
WiFi.disconnect(true); //disconnect form wifi to set new wifi connection
|
||||
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA); //init wifi mode
|
||||
|
||||
// Example1 (most common): a cert-file-free eduroam with PEAP (or TTLS)
|
||||
WiFi.begin(ssid, WPA2_AUTH_PEAP, EAP_IDENTITY, EAP_USERNAME, EAP_PASSWORD);
|
||||
|
||||
// Example 2: a cert-file WPA2 Enterprise with PEAP
|
||||
//WiFi.begin(ssid, WPA2_AUTH_PEAP, EAP_IDENTITY, EAP_USERNAME, EAP_PASSWORD, ca_pem, client_cert, client_key);
|
||||
|
||||
// Example 3: TLS with cert-files and no password
|
||||
//WiFi.begin(ssid, WPA2_AUTH_TLS, EAP_IDENTITY, NULL, NULL, ca_pem, client_cert, client_key);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
|
||||
delay(500);
|
||||
Serial.print(".");
|
||||
counter++;
|
||||
if(counter>=60){ //after 30 seconds timeout - reset board
|
||||
ESP.restart();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
Serial.println("");
|
||||
Serial.println("WiFi connected");
|
||||
Serial.println("IP address set: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); //print LAN IP
|
||||
}
|
||||
void loop() {
|
||||
if (WiFi.status() == WL_CONNECTED) { //if we are connected to Eduroam network
|
||||
counter = 0; //reset counter
|
||||
Serial.println("Wifi is still connected with IP: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); //inform user about his IP address
|
||||
}else if (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) { //if we lost connection, retry
|
||||
WiFi.begin(ssid);
|
||||
}
|
||||
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) { //during lost connection, print dots
|
||||
delay(500);
|
||||
Serial.print(".");
|
||||
counter++;
|
||||
if(counter>=60){ //30 seconds timeout - reset board
|
||||
ESP.restart();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
Serial.print("Connecting to website: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(host);
|
||||
WiFiClient client;
|
||||
if (client.connect(host, 80)) {
|
||||
String url = "/rele/rele1.txt";
|
||||
client.print(String("GET ") + url + " HTTP/1.1\r\n" + "Host: " + host + "\r\n" + "User-Agent: ESP32\r\n" + "Connection: close\r\n\r\n");
|
||||
|
||||
while (client.connected()) {
|
||||
String line = client.readStringUntil('\n');
|
||||
if (line == "\r") {
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
String line = client.readStringUntil('\n');
|
||||
Serial.println(line);
|
||||
}else{
|
||||
Serial.println("Connection unsucessful");
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
174
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiClientEvents/WiFiClientEvents.ino
Normal file
174
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiClientEvents/WiFiClientEvents.ino
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,174 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* This sketch shows the WiFi event usage
|
||||
*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* WiFi Events
|
||||
|
||||
0 ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_READY < ESP32 WiFi ready
|
||||
1 ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_SCAN_DONE < ESP32 finish scanning AP
|
||||
2 ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_START < ESP32 station start
|
||||
3 ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_STOP < ESP32 station stop
|
||||
4 ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_CONNECTED < ESP32 station connected to AP
|
||||
5 ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_DISCONNECTED < ESP32 station disconnected from AP
|
||||
6 ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_AUTHMODE_CHANGE < the auth mode of AP connected by ESP32 station changed
|
||||
7 ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_GOT_IP < ESP32 station got IP from connected AP
|
||||
8 ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_LOST_IP < ESP32 station lost IP and the IP is reset to 0
|
||||
9 ARDUINO_EVENT_WPS_ER_SUCCESS < ESP32 station wps succeeds in enrollee mode
|
||||
10 ARDUINO_EVENT_WPS_ER_FAILED < ESP32 station wps fails in enrollee mode
|
||||
11 ARDUINO_EVENT_WPS_ER_TIMEOUT < ESP32 station wps timeout in enrollee mode
|
||||
12 ARDUINO_EVENT_WPS_ER_PIN < ESP32 station wps pin code in enrollee mode
|
||||
13 ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_AP_START < ESP32 soft-AP start
|
||||
14 ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_AP_STOP < ESP32 soft-AP stop
|
||||
15 ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_AP_STACONNECTED < a station connected to ESP32 soft-AP
|
||||
16 ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_AP_STADISCONNECTED < a station disconnected from ESP32 soft-AP
|
||||
17 ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_AP_STAIPASSIGNED < ESP32 soft-AP assign an IP to a connected station
|
||||
18 ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_AP_PROBEREQRECVED < Receive probe request packet in soft-AP interface
|
||||
19 ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_AP_GOT_IP6 < ESP32 ap interface v6IP addr is preferred
|
||||
19 ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_GOT_IP6 < ESP32 station interface v6IP addr is preferred
|
||||
20 ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_START < ESP32 ethernet start
|
||||
21 ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_STOP < ESP32 ethernet stop
|
||||
22 ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_CONNECTED < ESP32 ethernet phy link up
|
||||
23 ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_DISCONNECTED < ESP32 ethernet phy link down
|
||||
24 ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_GOT_IP < ESP32 ethernet got IP from connected AP
|
||||
19 ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_GOT_IP6 < ESP32 ethernet interface v6IP addr is preferred
|
||||
25 ARDUINO_EVENT_MAX
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <WiFi.h>
|
||||
|
||||
const char* ssid = "your-ssid";
|
||||
const char* password = "your-password";
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
void WiFiEvent(WiFiEvent_t event)
|
||||
{
|
||||
Serial.printf("[WiFi-event] event: %d\n", event);
|
||||
|
||||
switch (event) {
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_READY:
|
||||
Serial.println("WiFi interface ready");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_SCAN_DONE:
|
||||
Serial.println("Completed scan for access points");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_START:
|
||||
Serial.println("WiFi client started");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_STOP:
|
||||
Serial.println("WiFi clients stopped");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_CONNECTED:
|
||||
Serial.println("Connected to access point");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_DISCONNECTED:
|
||||
Serial.println("Disconnected from WiFi access point");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_AUTHMODE_CHANGE:
|
||||
Serial.println("Authentication mode of access point has changed");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_GOT_IP:
|
||||
Serial.print("Obtained IP address: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_LOST_IP:
|
||||
Serial.println("Lost IP address and IP address is reset to 0");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WPS_ER_SUCCESS:
|
||||
Serial.println("WiFi Protected Setup (WPS): succeeded in enrollee mode");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WPS_ER_FAILED:
|
||||
Serial.println("WiFi Protected Setup (WPS): failed in enrollee mode");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WPS_ER_TIMEOUT:
|
||||
Serial.println("WiFi Protected Setup (WPS): timeout in enrollee mode");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WPS_ER_PIN:
|
||||
Serial.println("WiFi Protected Setup (WPS): pin code in enrollee mode");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_AP_START:
|
||||
Serial.println("WiFi access point started");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_AP_STOP:
|
||||
Serial.println("WiFi access point stopped");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_AP_STACONNECTED:
|
||||
Serial.println("Client connected");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_AP_STADISCONNECTED:
|
||||
Serial.println("Client disconnected");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_AP_STAIPASSIGNED:
|
||||
Serial.println("Assigned IP address to client");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_AP_PROBEREQRECVED:
|
||||
Serial.println("Received probe request");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_AP_GOT_IP6:
|
||||
Serial.println("AP IPv6 is preferred");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_GOT_IP6:
|
||||
Serial.println("STA IPv6 is preferred");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_GOT_IP6:
|
||||
Serial.println("Ethernet IPv6 is preferred");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_START:
|
||||
Serial.println("Ethernet started");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_STOP:
|
||||
Serial.println("Ethernet stopped");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_CONNECTED:
|
||||
Serial.println("Ethernet connected");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_DISCONNECTED:
|
||||
Serial.println("Ethernet disconnected");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_ETH_GOT_IP:
|
||||
Serial.println("Obtained IP address");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default: break;
|
||||
}}
|
||||
|
||||
void WiFiGotIP(WiFiEvent_t event, WiFiEventInfo_t info)
|
||||
{
|
||||
Serial.println("WiFi connected");
|
||||
Serial.println("IP address: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(IPAddress(info.got_ip.ip_info.ip.addr));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void setup()
|
||||
{
|
||||
Serial.begin(115200);
|
||||
|
||||
// delete old config
|
||||
WiFi.disconnect(true);
|
||||
|
||||
delay(1000);
|
||||
|
||||
// Examples of different ways to register wifi events
|
||||
WiFi.onEvent(WiFiEvent);
|
||||
WiFi.onEvent(WiFiGotIP, WiFiEvent_t::ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_GOT_IP);
|
||||
WiFiEventId_t eventID = WiFi.onEvent([](WiFiEvent_t event, WiFiEventInfo_t info){
|
||||
Serial.print("WiFi lost connection. Reason: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(info.wifi_sta_disconnected.reason);
|
||||
}, WiFiEvent_t::ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_DISCONNECTED);
|
||||
|
||||
// Remove WiFi event
|
||||
Serial.print("WiFi Event ID: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(eventID);
|
||||
// WiFi.removeEvent(eventID);
|
||||
|
||||
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.println();
|
||||
Serial.println();
|
||||
Serial.println("Wait for WiFi... ");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void loop()
|
||||
{
|
||||
delay(1000);
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Example of connection using Static IP
|
||||
by Evandro Luis Copercini
|
||||
Public domain - 2017
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <WiFi.h>
|
||||
|
||||
const char* ssid = "your_network_name";
|
||||
const char* password = "your_network_password";
|
||||
const char* host = "example.com";
|
||||
const char* url = "/index.html";
|
||||
|
||||
IPAddress local_IP(192, 168, 31, 115);
|
||||
IPAddress gateway(192, 168, 31, 1);
|
||||
IPAddress subnet(255, 255, 0, 0);
|
||||
IPAddress primaryDNS(8, 8, 8, 8); //optional
|
||||
IPAddress secondaryDNS(8, 8, 4, 4); //optional
|
||||
|
||||
void setup()
|
||||
{
|
||||
Serial.begin(115200);
|
||||
|
||||
if (!WiFi.config(local_IP, gateway, subnet, primaryDNS, secondaryDNS)) {
|
||||
Serial.println("STA Failed to configure");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
|
||||
Serial.println(ssid);
|
||||
|
||||
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
|
||||
|
||||
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
|
||||
delay(500);
|
||||
Serial.print(".");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.println("");
|
||||
Serial.println("WiFi connected!");
|
||||
Serial.print("IP address: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
|
||||
Serial.print("ESP Mac Address: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(WiFi.macAddress());
|
||||
Serial.print("Subnet Mask: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(WiFi.subnetMask());
|
||||
Serial.print("Gateway IP: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(WiFi.gatewayIP());
|
||||
Serial.print("DNS: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(WiFi.dnsIP());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void loop()
|
||||
{
|
||||
delay(5000);
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.print("connecting to ");
|
||||
Serial.println(host);
|
||||
|
||||
// Use WiFiClient class to create TCP connections
|
||||
WiFiClient client;
|
||||
const int httpPort = 80;
|
||||
if (!client.connect(host, httpPort)) {
|
||||
Serial.println("connection failed");
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.print("Requesting URL: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(url);
|
||||
|
||||
// This will send the request to the server
|
||||
client.print(String("GET ") + url + " HTTP/1.1\r\n" +
|
||||
"Host: " + host + "\r\n" +
|
||||
"Connection: close\r\n\r\n");
|
||||
unsigned long timeout = millis();
|
||||
while (client.available() == 0) {
|
||||
if (millis() - timeout > 5000) {
|
||||
Serial.println(">>> Client Timeout !");
|
||||
client.stop();
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Read all the lines of the reply from server and print them to Serial
|
||||
while (client.available()) {
|
||||
String line = client.readStringUntil('\r');
|
||||
Serial.print(line);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.println();
|
||||
Serial.println("closing connection");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
120
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiIPv6/WiFiIPv6.ino
Normal file
120
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiIPv6/WiFiIPv6.ino
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,120 @@
|
||||
#include "WiFi.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#define STA_SSID "**********"
|
||||
#define STA_PASS "**********"
|
||||
#define AP_SSID "esp32-v6"
|
||||
|
||||
static volatile bool wifi_connected = false;
|
||||
|
||||
WiFiUDP ntpClient;
|
||||
|
||||
void wifiOnConnect(){
|
||||
Serial.println("STA Connected");
|
||||
Serial.print("STA IPv4: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
|
||||
|
||||
ntpClient.begin(2390);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void wifiOnDisconnect(){
|
||||
Serial.println("STA Disconnected");
|
||||
delay(1000);
|
||||
WiFi.begin(STA_SSID, STA_PASS);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void wifiConnectedLoop(){
|
||||
//lets check the time
|
||||
const int NTP_PACKET_SIZE = 48;
|
||||
byte ntpPacketBuffer[NTP_PACKET_SIZE];
|
||||
|
||||
IPAddress address;
|
||||
WiFi.hostByName("time.nist.gov", address);
|
||||
memset(ntpPacketBuffer, 0, NTP_PACKET_SIZE);
|
||||
ntpPacketBuffer[0] = 0b11100011; // LI, Version, Mode
|
||||
ntpPacketBuffer[1] = 0; // Stratum, or type of clock
|
||||
ntpPacketBuffer[2] = 6; // Polling Interval
|
||||
ntpPacketBuffer[3] = 0xEC; // Peer Clock Precision
|
||||
// 8 bytes of zero for Root Delay & Root Dispersion
|
||||
ntpPacketBuffer[12] = 49;
|
||||
ntpPacketBuffer[13] = 0x4E;
|
||||
ntpPacketBuffer[14] = 49;
|
||||
ntpPacketBuffer[15] = 52;
|
||||
ntpClient.beginPacket(address, 123); //NTP requests are to port 123
|
||||
ntpClient.write(ntpPacketBuffer, NTP_PACKET_SIZE);
|
||||
ntpClient.endPacket();
|
||||
|
||||
delay(1000);
|
||||
|
||||
int packetLength = ntpClient.parsePacket();
|
||||
if (packetLength){
|
||||
if(packetLength >= NTP_PACKET_SIZE){
|
||||
ntpClient.read(ntpPacketBuffer, NTP_PACKET_SIZE);
|
||||
}
|
||||
ntpClient.flush();
|
||||
uint32_t secsSince1900 = (uint32_t)ntpPacketBuffer[40] << 24 | (uint32_t)ntpPacketBuffer[41] << 16 | (uint32_t)ntpPacketBuffer[42] << 8 | ntpPacketBuffer[43];
|
||||
//Serial.printf("Seconds since Jan 1 1900: %u\n", secsSince1900);
|
||||
uint32_t epoch = secsSince1900 - 2208988800UL;
|
||||
//Serial.printf("EPOCH: %u\n", epoch);
|
||||
uint8_t h = (epoch % 86400L) / 3600;
|
||||
uint8_t m = (epoch % 3600) / 60;
|
||||
uint8_t s = (epoch % 60);
|
||||
Serial.printf("UTC: %02u:%02u:%02u (GMT)\n", h, m, s);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
delay(9000);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void WiFiEvent(WiFiEvent_t event){
|
||||
switch(event) {
|
||||
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_AP_START:
|
||||
//can set ap hostname here
|
||||
WiFi.softAPsetHostname(AP_SSID);
|
||||
//enable ap ipv6 here
|
||||
WiFi.softAPenableIpV6();
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_START:
|
||||
//set sta hostname here
|
||||
WiFi.setHostname(AP_SSID);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_CONNECTED:
|
||||
//enable sta ipv6 here
|
||||
WiFi.enableIpV6();
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_GOT_IP6:
|
||||
Serial.print("STA IPv6: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(WiFi.localIPv6());
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_AP_GOT_IP6:
|
||||
Serial.print("AP IPv6: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(WiFi.softAPIPv6());
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_GOT_IP:
|
||||
wifiOnConnect();
|
||||
wifi_connected = true;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_DISCONNECTED:
|
||||
wifi_connected = false;
|
||||
wifiOnDisconnect();
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void setup(){
|
||||
Serial.begin(115200);
|
||||
WiFi.disconnect(true);
|
||||
WiFi.onEvent(WiFiEvent);
|
||||
WiFi.mode(WIFI_MODE_APSTA);
|
||||
WiFi.softAP(AP_SSID);
|
||||
WiFi.begin(STA_SSID, STA_PASS);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void loop(){
|
||||
if(wifi_connected){
|
||||
wifiConnectedLoop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
while(Serial.available()) Serial.write(Serial.read());
|
||||
}
|
||||
35
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiMulti/WiFiMulti.ino
Normal file
35
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiMulti/WiFiMulti.ino
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* This sketch trys to Connect to the best AP based on a given list
|
||||
*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <WiFi.h>
|
||||
#include <WiFiMulti.h>
|
||||
|
||||
WiFiMulti wifiMulti;
|
||||
|
||||
void setup()
|
||||
{
|
||||
Serial.begin(115200);
|
||||
delay(10);
|
||||
|
||||
wifiMulti.addAP("ssid_from_AP_1", "your_password_for_AP_1");
|
||||
wifiMulti.addAP("ssid_from_AP_2", "your_password_for_AP_2");
|
||||
wifiMulti.addAP("ssid_from_AP_3", "your_password_for_AP_3");
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.println("Connecting Wifi...");
|
||||
if(wifiMulti.run() == WL_CONNECTED) {
|
||||
Serial.println("");
|
||||
Serial.println("WiFi connected");
|
||||
Serial.println("IP address: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void loop()
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(wifiMulti.run() != WL_CONNECTED) {
|
||||
Serial.println("WiFi not connected!");
|
||||
delay(1000);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
73
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiScan/README.md
Normal file
73
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiScan/README.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
|
||||
# WiFiScan Example
|
||||
|
||||
This example demonstrates how to use the WiFi library to scan available WiFi networks and print the results.
|
||||
|
||||
# Supported Targets
|
||||
|
||||
Currently this example supports the following targets.
|
||||
|
||||
| Supported Targets | ESP32 | ESP32-S2 | ESP32-C3 |
|
||||
| ----------------- | ----- | -------- | -------- |
|
||||
|
||||
## How to Use Example
|
||||
|
||||
* How to install the Arduino IDE: [Install Arduino IDE](https://github.com/espressif/arduino-esp32/tree/master/docs/arduino-ide).
|
||||
|
||||
#### Using Arduino IDE
|
||||
|
||||
* Before Compile/Verify, select the correct board: `Tools -> Board`.
|
||||
* Select the COM port: `Tools -> Port: xxx` where the `xxx` is the detected COM port.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Using Platform IO
|
||||
|
||||
* Select the COM port: `Devices` or setting the `upload_port` option on the `platformio.ini` file.
|
||||
|
||||
## Example/Log Output
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ets Jul 29 2019 12:21:46
|
||||
|
||||
rst:0x1 (POWERON_RESET),boot:0x13 (SPI_FAST_FLASH_BOOT)
|
||||
configsip: 0, SPIWP:0xee
|
||||
clk_drv:0x00,q_drv:0x00,d_drv:0x00,cs0_drv:0x00,hd_drv:0x00,wp_drv:0x00
|
||||
mode:DIO, clock div:1
|
||||
load:0x3fff0030,len:1412
|
||||
load:0x40078000,len:13400
|
||||
load:0x40080400,len:3672
|
||||
entry 0x400805f8
|
||||
Setup done
|
||||
scan start
|
||||
scan done
|
||||
17 networks found
|
||||
1: IoTNetwork (-62)*
|
||||
2: WiFiSSID (-62)*
|
||||
3: B3A7992 (-63)*
|
||||
4: WiFi (-63)
|
||||
5: IoTNetwork2 (-64)*
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Troubleshooting
|
||||
|
||||
***Important: Be sure you're using a good quality USB cable and you have enought power source for your project.***
|
||||
|
||||
* **Programming Fail:** If the programming/flash procedure fails, try to reduce the serial connection speed.
|
||||
* **COM port not detected:** Check the USB cable connection and the USB to Serial driver installation.
|
||||
|
||||
If the error persist, you can ask help at the official [ESP32 forum](https://esp32.com) or see [Contribute](#contribute).
|
||||
|
||||
## Contribute
|
||||
|
||||
To know how to contribute to this project, see [How to contribute.](https://github.com/espressif/arduino-esp32/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.rst)
|
||||
|
||||
If you have any **feedback** or **issue** to report on this example/library, please open an issue or fix it by creating a new PR. Contributions are more than welcome!
|
||||
|
||||
Before creating a new issue, be sure to try the Troubleshooting and to check if the same issue was already created by someone else.
|
||||
|
||||
## Resources
|
||||
|
||||
* Arduino-ESP32 Official Repository: [espressif/arduino-esp32](https://github.com/espressif/arduino-esp32)
|
||||
* ESP32 Datasheet: [Link to datasheet](https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp32_datasheet_en.pdf)
|
||||
* ESP32-S2 Datasheet: [Link to datasheet](https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp32-s2_datasheet_en.pdf)
|
||||
* ESP32-C3 Datasheet: [Link to datasheet](https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp32-c3_datasheet_en.pdf)
|
||||
* Official ESP-IDF documentation: [ESP-IDF](https://idf.espressif.com)
|
||||
48
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiScan/WiFiScan.ino
Normal file
48
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiScan/WiFiScan.ino
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* This sketch demonstrates how to scan WiFi networks.
|
||||
* The API is almost the same as with the WiFi Shield library,
|
||||
* the most obvious difference being the different file you need to include:
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#include "WiFi.h"
|
||||
|
||||
void setup()
|
||||
{
|
||||
Serial.begin(115200);
|
||||
|
||||
// Set WiFi to station mode and disconnect from an AP if it was previously connected
|
||||
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
|
||||
WiFi.disconnect();
|
||||
delay(100);
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.println("Setup done");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void loop()
|
||||
{
|
||||
Serial.println("scan start");
|
||||
|
||||
// WiFi.scanNetworks will return the number of networks found
|
||||
int n = WiFi.scanNetworks();
|
||||
Serial.println("scan done");
|
||||
if (n == 0) {
|
||||
Serial.println("no networks found");
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
Serial.print(n);
|
||||
Serial.println(" networks found");
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
|
||||
// Print SSID and RSSI for each network found
|
||||
Serial.print(i + 1);
|
||||
Serial.print(": ");
|
||||
Serial.print(WiFi.SSID(i));
|
||||
Serial.print(" (");
|
||||
Serial.print(WiFi.RSSI(i));
|
||||
Serial.print(")");
|
||||
Serial.println((WiFi.encryptionType(i) == WIFI_AUTH_OPEN)?" ":"*");
|
||||
delay(10);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
Serial.println("");
|
||||
|
||||
// Wait a bit before scanning again
|
||||
delay(5000);
|
||||
}
|
||||
70
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiScanDualAntenna/README.md
Normal file
70
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiScanDualAntenna/README.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
||||
# WiFiScan Example
|
||||
|
||||
This example demonstrates how to use the WiFi library to scan available WiFi networks and print the results.
|
||||
|
||||
This example shows the basic functionality of the dual antenna capability.
|
||||
|
||||
# Supported Targets
|
||||
|
||||
This example is compatible with the ESP32-WROOM-DA.
|
||||
|
||||
## How to Use Example
|
||||
|
||||
* How to install the Arduino IDE: [Install Arduino IDE](https://github.com/espressif/arduino-esp32/tree/master/docs/arduino-ide).
|
||||
|
||||
#### Using Arduino IDE
|
||||
|
||||
* Before Compile/Verify, select the correct board: `Tools -> Board`.
|
||||
* Select the COM port: `Tools -> Port: xxx` where the `xxx` is the detected COM port.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Using Platform IO
|
||||
|
||||
* Select the COM port: `Devices` or set the `upload_port` option on the `platformio.ini` file.
|
||||
|
||||
## Example/Log Output
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ets Jul 29 2019 12:21:46
|
||||
|
||||
rst:0x1 (POWERON_RESET),boot:0x13 (SPI_FAST_FLASH_BOOT)
|
||||
configsip: 0, SPIWP:0xee
|
||||
clk_drv:0x00,q_drv:0x00,d_drv:0x00,cs0_drv:0x00,hd_drv:0x00,wp_drv:0x00
|
||||
mode:DIO, clock div:1
|
||||
load:0x3fff0030,len:1412
|
||||
load:0x40078000,len:13400
|
||||
load:0x40080400,len:3672
|
||||
entry 0x400805f8
|
||||
Setup done
|
||||
scan start
|
||||
scan done
|
||||
17 networks found
|
||||
1: IoTNetwork (-62)*
|
||||
2: WiFiSSID (-62)*
|
||||
3: B3A7992 (-63)*
|
||||
4: WiFi (-63)
|
||||
5: IoTNetwork2 (-64)*
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Troubleshooting
|
||||
|
||||
***Important: Be sure you're using a good quality USB cable and you have enough power source for your project.***
|
||||
|
||||
* **Programming Fail:** If the programming/flash procedure fails, try to reduce the serial connection speed.
|
||||
* **COM port not detected:** Check the USB cable connection and the USB to Serial driver installation.
|
||||
|
||||
If the error persists, you can ask for help at the official [ESP32 forum](https://esp32.com) or see [Contribute](#contribute).
|
||||
|
||||
## Contribute
|
||||
|
||||
To know how to contribute to this project, see [How to contribute.](https://github.com/espressif/arduino-esp32/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.rst)
|
||||
|
||||
If you have any **feedback** or **issue** to report on this example/library, please open an issue or fix it by creating a new PR. Contributions are more than welcome!
|
||||
|
||||
Before creating a new issue, be sure to try the Troubleshooting and to check if the same issue was already created by someone else.
|
||||
|
||||
## Resources
|
||||
|
||||
* Arduino-ESP32 Official Repository: [espressif/arduino-esp32](https://github.com/espressif/arduino-esp32)
|
||||
* ESP32 Datasheet: [Link to datasheet](https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp32_datasheet_en.pdf)
|
||||
* ESP32-WROOM-DA Datasheet: [Link to datasheet](https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp32-wroom-da_datasheet_en.pdf)
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* This sketch demonstrates how to scan WiFi networks.
|
||||
* The API is almost the same as with the WiFi Shield library,
|
||||
* the most obvious difference being the different file you need to include:
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#include "WiFi.h"
|
||||
|
||||
/* These are the GPIOs connected to the antenna switch on the ESP32-WROOM-DA.
|
||||
* Both GPIOs are not exposed to the module pins and cannot be used except to
|
||||
* control the antnnas switch.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* For more details, see the datashhet at:
|
||||
* https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp32-wroom-da_datasheet_en.pdf
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#define GPIO_ANT1 2 // GPIO for antenna 1
|
||||
#define GPIO_ANT2 25 // GPIO for antenna 2 (default)
|
||||
|
||||
void setup()
|
||||
{
|
||||
bool err = false;
|
||||
Serial.begin(115200);
|
||||
|
||||
// Set WiFi to station mode and disconnect from an AP if it was previously connected
|
||||
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Attention: This is the manual prodecure for the dual antenna configuration.
|
||||
* If you choose the ESP32-WROOM-DA module from the Tools -> Board, this configuration
|
||||
* is not necessary!
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Set WiFi dual antenna configuration by passing the GPIO and antenna mode for RX ant TX
|
||||
*/
|
||||
err = WiFi.setDualAntennaConfig(GPIO_ANT1, GPIO_ANT2, WIFI_RX_ANT_AUTO, WIFI_TX_ANT_AUTO);
|
||||
|
||||
/* For more details on how to use this feature, see our docs:
|
||||
* https://docs.espressif.com/projects/arduino-esp32/en/latest/api/wifi.html
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
if(err == false) {
|
||||
Serial.println("Dual Antenna configuration failed!");
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
Serial.println("Dual Antenna configuration successfuly done!");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
WiFi.disconnect();
|
||||
delay(100);
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.println("Setup done");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void loop()
|
||||
{
|
||||
Serial.println("scan start");
|
||||
|
||||
// WiFi.scanNetworks will return the number of networks found
|
||||
int n = WiFi.scanNetworks();
|
||||
Serial.println("scan done");
|
||||
if (n == 0) {
|
||||
Serial.println("no networks found");
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
Serial.print(n);
|
||||
Serial.println(" networks found");
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
|
||||
// Print SSID and RSSI for each network found
|
||||
Serial.print(i + 1);
|
||||
Serial.print(": ");
|
||||
Serial.print(WiFi.SSID(i));
|
||||
Serial.print(" (");
|
||||
Serial.print(WiFi.RSSI(i));
|
||||
Serial.print(")");
|
||||
Serial.println((WiFi.encryptionType(i) == WIFI_AUTH_OPEN)?" ":"*");
|
||||
delay(10);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
Serial.println("");
|
||||
|
||||
// Wait a bit before scanning again
|
||||
delay(5000);
|
||||
}
|
||||
36
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiSmartConfig/WiFiSmartConfig.ino
Normal file
36
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiSmartConfig/WiFiSmartConfig.ino
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
#include "WiFi.h"
|
||||
|
||||
void setup() {
|
||||
Serial.begin(115200);
|
||||
|
||||
//Init WiFi as Station, start SmartConfig
|
||||
WiFi.mode(WIFI_AP_STA);
|
||||
WiFi.beginSmartConfig();
|
||||
|
||||
//Wait for SmartConfig packet from mobile
|
||||
Serial.println("Waiting for SmartConfig.");
|
||||
while (!WiFi.smartConfigDone()) {
|
||||
delay(500);
|
||||
Serial.print(".");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.println("");
|
||||
Serial.println("SmartConfig received.");
|
||||
|
||||
//Wait for WiFi to connect to AP
|
||||
Serial.println("Waiting for WiFi");
|
||||
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
|
||||
delay(500);
|
||||
Serial.print(".");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.println("WiFi Connected.");
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.print("IP Address: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void loop() {
|
||||
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,129 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
WiFiTelnetToSerial - Example Transparent UART to Telnet Server for ESP32
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2017 Hristo Gochkov. All rights reserved.
|
||||
This file is part of the ESP32 WiFi library for Arduino environment.
|
||||
|
||||
This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||
modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||
License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||
version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||
|
||||
This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||
Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||
License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||
Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#include <WiFi.h>
|
||||
#include <WiFiMulti.h>
|
||||
|
||||
WiFiMulti wifiMulti;
|
||||
|
||||
//how many clients should be able to telnet to this ESP32
|
||||
#define MAX_SRV_CLIENTS 1
|
||||
const char* ssid = "**********";
|
||||
const char* password = "**********";
|
||||
|
||||
WiFiServer server(23);
|
||||
WiFiClient serverClients[MAX_SRV_CLIENTS];
|
||||
|
||||
void setup() {
|
||||
Serial.begin(115200);
|
||||
Serial.println("\nConnecting");
|
||||
|
||||
wifiMulti.addAP(ssid, password);
|
||||
wifiMulti.addAP("ssid_from_AP_2", "your_password_for_AP_2");
|
||||
wifiMulti.addAP("ssid_from_AP_3", "your_password_for_AP_3");
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.println("Connecting Wifi ");
|
||||
for (int loops = 10; loops > 0; loops--) {
|
||||
if (wifiMulti.run() == WL_CONNECTED) {
|
||||
Serial.println("");
|
||||
Serial.print("WiFi connected ");
|
||||
Serial.print("IP address: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else {
|
||||
Serial.println(loops);
|
||||
delay(1000);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (wifiMulti.run() != WL_CONNECTED) {
|
||||
Serial.println("WiFi connect failed");
|
||||
delay(1000);
|
||||
ESP.restart();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//start UART and the server
|
||||
Serial1.begin(9600);
|
||||
server.begin();
|
||||
server.setNoDelay(true);
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.print("Ready! Use 'telnet ");
|
||||
Serial.print(WiFi.localIP());
|
||||
Serial.println(" 23' to connect");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void loop() {
|
||||
uint8_t i;
|
||||
if (wifiMulti.run() == WL_CONNECTED) {
|
||||
//check if there are any new clients
|
||||
if (server.hasClient()){
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < MAX_SRV_CLIENTS; i++){
|
||||
//find free/disconnected spot
|
||||
if (!serverClients[i] || !serverClients[i].connected()){
|
||||
if(serverClients[i]) serverClients[i].stop();
|
||||
serverClients[i] = server.available();
|
||||
if (!serverClients[i]) Serial.println("available broken");
|
||||
Serial.print("New client: ");
|
||||
Serial.print(i); Serial.print(' ');
|
||||
Serial.println(serverClients[i].remoteIP());
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (i >= MAX_SRV_CLIENTS) {
|
||||
//no free/disconnected spot so reject
|
||||
server.available().stop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
//check clients for data
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < MAX_SRV_CLIENTS; i++){
|
||||
if (serverClients[i] && serverClients[i].connected()){
|
||||
if(serverClients[i].available()){
|
||||
//get data from the telnet client and push it to the UART
|
||||
while(serverClients[i].available()) Serial1.write(serverClients[i].read());
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
else {
|
||||
if (serverClients[i]) {
|
||||
serverClients[i].stop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
//check UART for data
|
||||
if(Serial1.available()){
|
||||
size_t len = Serial1.available();
|
||||
uint8_t sbuf[len];
|
||||
Serial1.readBytes(sbuf, len);
|
||||
//push UART data to all connected telnet clients
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < MAX_SRV_CLIENTS; i++){
|
||||
if (serverClients[i] && serverClients[i].connected()){
|
||||
serverClients[i].write(sbuf, len);
|
||||
delay(1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
else {
|
||||
Serial.println("WiFi not connected!");
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < MAX_SRV_CLIENTS; i++) {
|
||||
if (serverClients[i]) serverClients[i].stop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
delay(1000);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
76
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiUDPClient/WiFiUDPClient.ino
Normal file
76
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiUDPClient/WiFiUDPClient.ino
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* This sketch sends random data over UDP on a ESP32 device
|
||||
*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#include <WiFi.h>
|
||||
#include <WiFiUdp.h>
|
||||
|
||||
// WiFi network name and password:
|
||||
const char * networkName = "your-ssid";
|
||||
const char * networkPswd = "your-password";
|
||||
|
||||
//IP address to send UDP data to:
|
||||
// either use the ip address of the server or
|
||||
// a network broadcast address
|
||||
const char * udpAddress = "192.168.0.255";
|
||||
const int udpPort = 3333;
|
||||
|
||||
//Are we currently connected?
|
||||
boolean connected = false;
|
||||
|
||||
//The udp library class
|
||||
WiFiUDP udp;
|
||||
|
||||
void setup(){
|
||||
// Initilize hardware serial:
|
||||
Serial.begin(115200);
|
||||
|
||||
//Connect to the WiFi network
|
||||
connectToWiFi(networkName, networkPswd);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void loop(){
|
||||
//only send data when connected
|
||||
if(connected){
|
||||
//Send a packet
|
||||
udp.beginPacket(udpAddress,udpPort);
|
||||
udp.printf("Seconds since boot: %lu", millis()/1000);
|
||||
udp.endPacket();
|
||||
}
|
||||
//Wait for 1 second
|
||||
delay(1000);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void connectToWiFi(const char * ssid, const char * pwd){
|
||||
Serial.println("Connecting to WiFi network: " + String(ssid));
|
||||
|
||||
// delete old config
|
||||
WiFi.disconnect(true);
|
||||
//register event handler
|
||||
WiFi.onEvent(WiFiEvent);
|
||||
|
||||
//Initiate connection
|
||||
WiFi.begin(ssid, pwd);
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.println("Waiting for WIFI connection...");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//wifi event handler
|
||||
void WiFiEvent(WiFiEvent_t event){
|
||||
switch(event) {
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_GOT_IP:
|
||||
//When connected set
|
||||
Serial.print("WiFi connected! IP address: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
|
||||
//initializes the UDP state
|
||||
//This initializes the transfer buffer
|
||||
udp.begin(WiFi.localIP(),udpPort);
|
||||
connected = true;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case ARDUINO_EVENT_WIFI_STA_DISCONNECTED:
|
||||
Serial.println("WiFi lost connection");
|
||||
connected = false;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default: break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
30
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiUDPClient/udp_server.py
Normal file
30
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiUDPClient/udp_server.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
# This python script listens on UDP port 3333
|
||||
# for messages from the ESP32 board and prints them
|
||||
import socket
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
|
||||
try :
|
||||
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
|
||||
s.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
|
||||
except socket.error, msg :
|
||||
print 'Failed to create socket. Error Code : ' + str(msg[0]) + ' Message ' + msg[1]
|
||||
sys.exit()
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
s.bind(('', 3333))
|
||||
except socket.error , msg:
|
||||
print 'Bind failed. Error: ' + str(msg[0]) + ': ' + msg[1]
|
||||
sys.exit()
|
||||
|
||||
print 'Server listening'
|
||||
|
||||
while 1:
|
||||
d = s.recvfrom(1024)
|
||||
data = d[0]
|
||||
|
||||
if not data:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
print data.strip()
|
||||
|
||||
s.close()
|
||||
16
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiUDPClient/udp_server.rb
Normal file
16
libraries/WiFi/examples/WiFiUDPClient/udp_server.rb
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
||||
# This ruby script listens on UDP port 3333
|
||||
# for messages from the ESP32 board and prints them
|
||||
|
||||
require 'socket'
|
||||
include Socket::Constants
|
||||
|
||||
udp_socket = UDPSocket.new(AF_INET)
|
||||
|
||||
#bind
|
||||
udp_socket.bind("", 3333)
|
||||
puts 'Server listening'
|
||||
|
||||
while true do
|
||||
message, sender = udp_socket.recvfrom(1024)
|
||||
puts message
|
||||
end
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user